

It is important for the examining physician to obtain a detailed history and physical exam, which can be often difficult in the young, non-cooperative, injured child.(Hatch 2003) Evaluation of the point of maximal tenderness and close evaluation of the integrity of the skin around the toe should be performed to ensure that there is not a nail-bed injury. They can present with localized pain to the affected toe, a limp or with the inability to weight bear. Pediatric patients with phalanx fractures have a broad presentation. Phalangeal fractures represent 3% to 7% of all physeal fractures and are usually Salter-Harris type I or type II injuries.(Kay 2001) Pediatric phalanx fractures are more common in boys than girls and are most commonly closed injuries. Fractures of the toes represent the most common foot fractures in the pediatric age group and may account for as many as 18% of pediatric foot fractures. Fractures of the foot account for approximately 5% to 13% of all pediatric fractures. Pediatric phalanx fractures are one of the most common fractures in children. The vast majority of pediatric foot fractures do well with non-operative management.(Kay 2001) Surgical treatment is recommended for open fractures, significantly displaced fractures, and displaced intra-articular fractures of the hallux. Displaced intra-articular fractures of the hallux require reductionįractures of the phalanx are the most common type of foot fractures in the pediatric population.Nail-bed injuries involving the germinal matrix should be repaired.Open fractures require irrigation & debridement.Often not treated by orthopedic surgeons.One of the most common foot fractures in children.
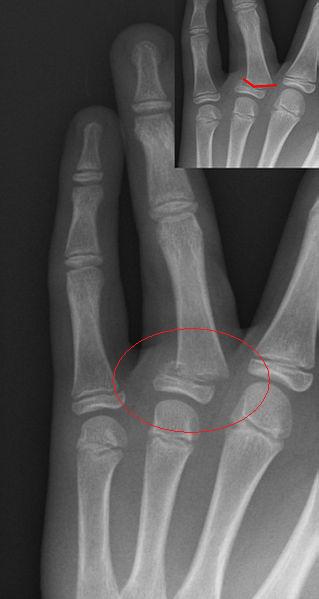
Study Guide Foot Fractures - Phalanx Key Points:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
